Material Topics Impact Assessment and Value Chain Mapping
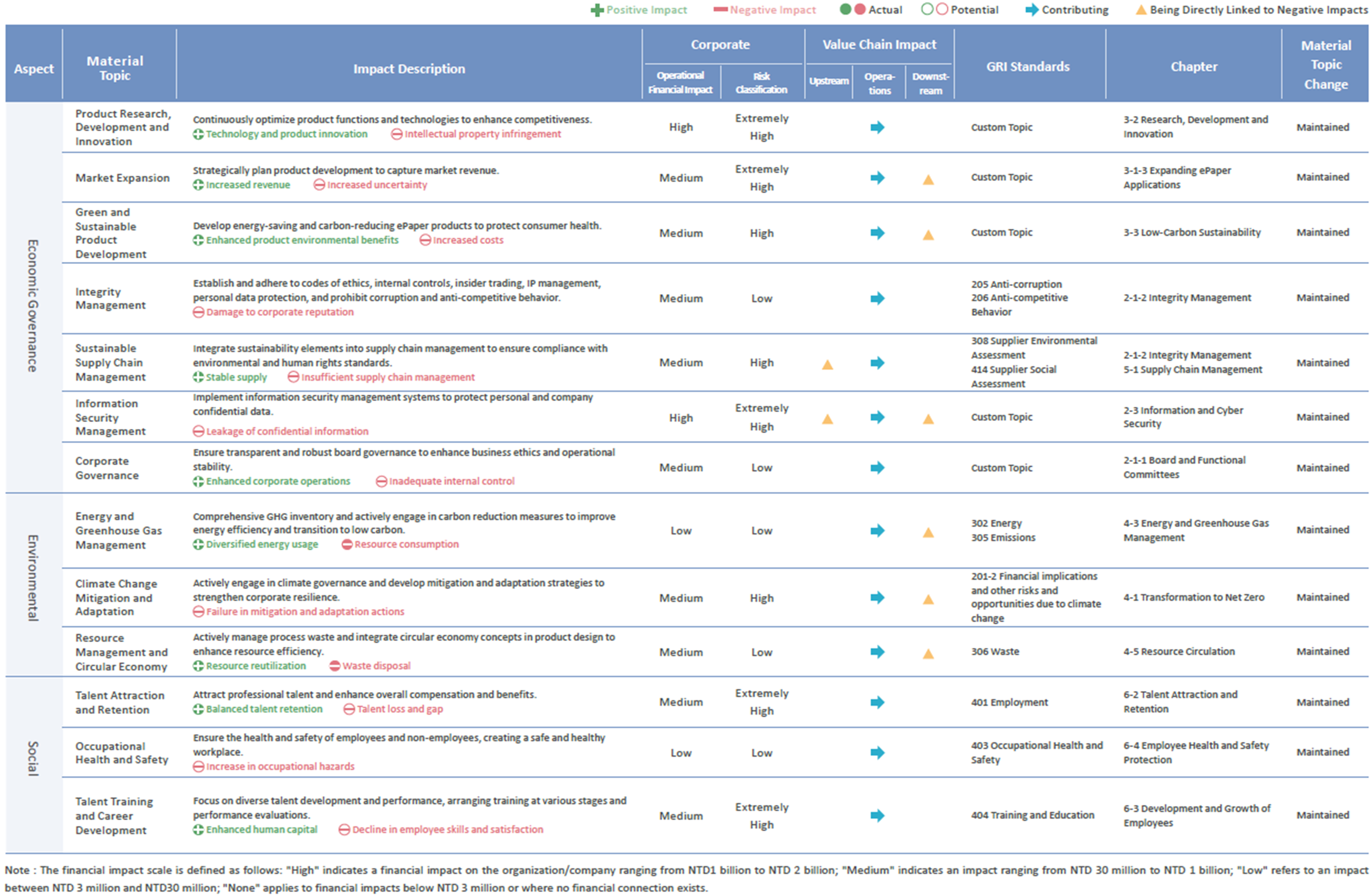
Material Topics Impact Assessment

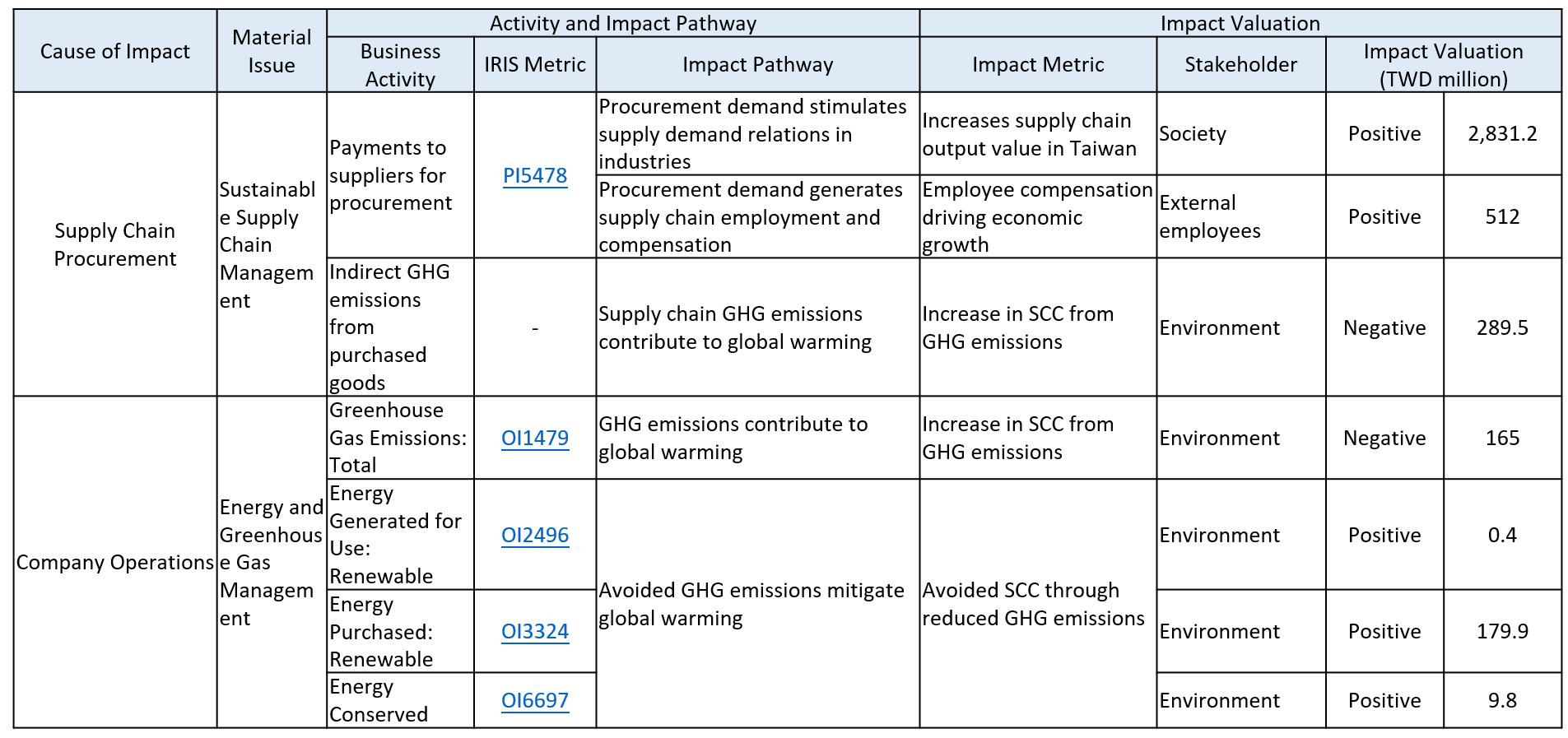
Sustainability Impact Valuation Table
To better understand the potential negative impacts of material issues on external stakeholders, E Ink conducted a Sustainability Impact Valuation Analysis. This systematic approach assesses the externalities generated by business operations and supply chain activities. For this round of analysis, priority was given to two material topics: Sustainable Supply Chain Management and Energy and Greenhouse Gas Management. Moving forward, the Company will continue to assess the impacts of other material topics, gradually building a comprehensive impact framework. This ensures that while pursuing business growth, E Ink actively responds to stakeholder concerns and mitigates potential environmental and social impacts.
Suppliers are indispensable partners in building E Ink’s sustainable value chain. They play a vital role in advancing business development and implementing sustainability management. E Ink firmly believes that through close engagement with suppliers, the Company can not only enhance operational efficiency but also expand its positive influence on external stakeholders.
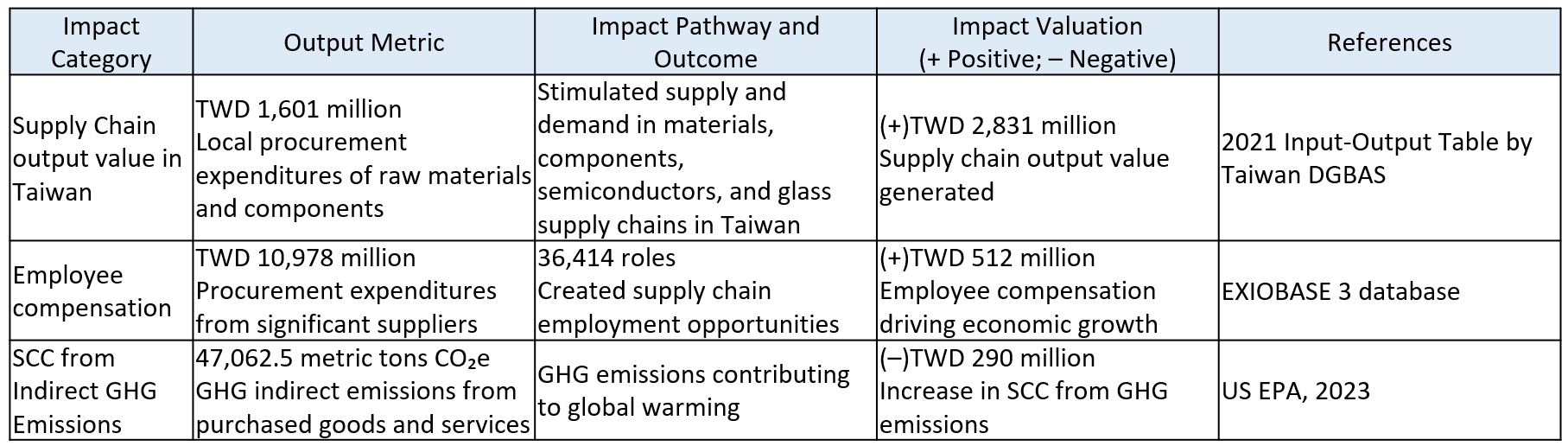
For Sustainable Supply Chain Management, payments to suppliers for procurement generate positive external impacts. Procurement demand stimulates supply-demand relations across multiple industries, strengthening economic linkages, driving industrial development, and contributing directly to societal well-being. At the same time, procurement creates employment opportunities and compensation throughout the supply chain, which are materially relevant to external employees by supporting livelihoods, enhancing income growth, and fostering economic resilience.
Conversely, indirect greenhouse gas emissions from purchased goods create negative externalities that are materially relevant to the environment. These emissions directly contribute to global warming and impose long-term costs on natural systems. The Social Cost of Carbon (SCC) is used to measure the economic damages caused by each metric ton of greenhouse gas emissions, capturing broad environmental consequences such as impacts on ecosystems, climate stability, and societal well-being. Applying SCC highlights the substantial environmental relevance of procurement-related emissions and underscores the importance of managing supply chain carbon impacts responsibly.
In 2024, E Ink adopted the “Domestic Interindustry Linkage Table” published by Taiwan’s Directorate General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics (DGBAS, 2021), combined with the EXIOBASE 3 databaseNote 1, applying the Input-Output Model to conduct quantitative analysis. This assessment evaluates supply chain output value, employment, and employee compensation generated by the Company’s supply chain procurement expenditures. In addition, the social cost of carbon (SCC) Note 2 was used to estimate the environment impacts of indirect greenhouse gas emissions resulting from the procurement of goods and services. The analysis results serve as a critical reference for E Ink’s future risk management and strategic planning, supporting deeper sustainable partnerships with suppliers to jointly reduce potential impacts of the supply chain on stakeholders and the environment, while steadily progressing toward the goal of a “sustainable and value-added supply chain.”
To mitigate environmental impacts arising from the supply chain, E Ink also adopted ISO 20400 in 2024, while encouraging significant suppliers to set carbon reduction targets, strengthen packaging recycling mechanisms, and enhance training programs. Together, these measures aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and achieve the company’s target of reducing Scope 3 emissions by 25% from a 2021 baseline.
Note 1: EXIOBASE is a global, high-resolution, multi-regional environmentally extended input-output database (EE-MRIO) jointly developed by multiple European research institutions. It integrates multi-regional supply-use tables (MR-SUT) and multi-regional input-output tables (MR-IOT) to assess the overall environmental and resource impacts of product consumption. The latest version, EXIOBASE 3, is one of the most comprehensive EE-MRIO systems worldwide. Its core structure is built on rectangular supply-use tables covering 163 industries and 200 products. The database includes data for 44 countries (28 EU member states and 16 major economies) as well as five aggregated “Rest of World” regions. EXIOBASE 3 consolidates a wide range of environmental and social indicators, including carbon emissions, water resources, land use, energy consumption, employment, and employee compensation. It is widely applied by corporations and research institutions to analyze the environmental impacts and social benefits of final product consumption, serving as an essential tool for evaluating carbon footprints, water footprints, job creation, and income contributions within sustainability impact assessments.
Note 2: The Social Cost of Carbon (SCC), expressed in 2020 US dollars, measures the long-term economic damages caused by one metric ton of greenhouse gas emissions. According to the US Environmental Protection Agency’s (US EPA, 2023) latest methodology, the SCC integrates four modules: socioeconomic, climate, damage, and discount rate, while combining multiple damage functions and discount rate scenarios for comprehensive evaluation. Major categories of damages include heat- and cold-related mortality, energy expenditures, labor productivity, agriculture, and coastal damages. The results show that climate change will increase pressure on both physical and economic systems, with incremental losses from future emissions continuing to rise. In the 2023 update of the “EPA Report on the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases” methodology released by the US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA), it provided three dynamic Ramsey discount rates: 1.5%, 2.0%, and 2.5%. Among these, 2.0% was designated as the core scenario and the official recommended value, as it balances responsibility to future generations while avoiding extreme valuations. Therefore, this analysis adopts USD 208 per metric ton of CO₂ (2020 value) at a 2.0% discount rate as the primary valuation basis, ensuring alignment with mainstream international methodologies.
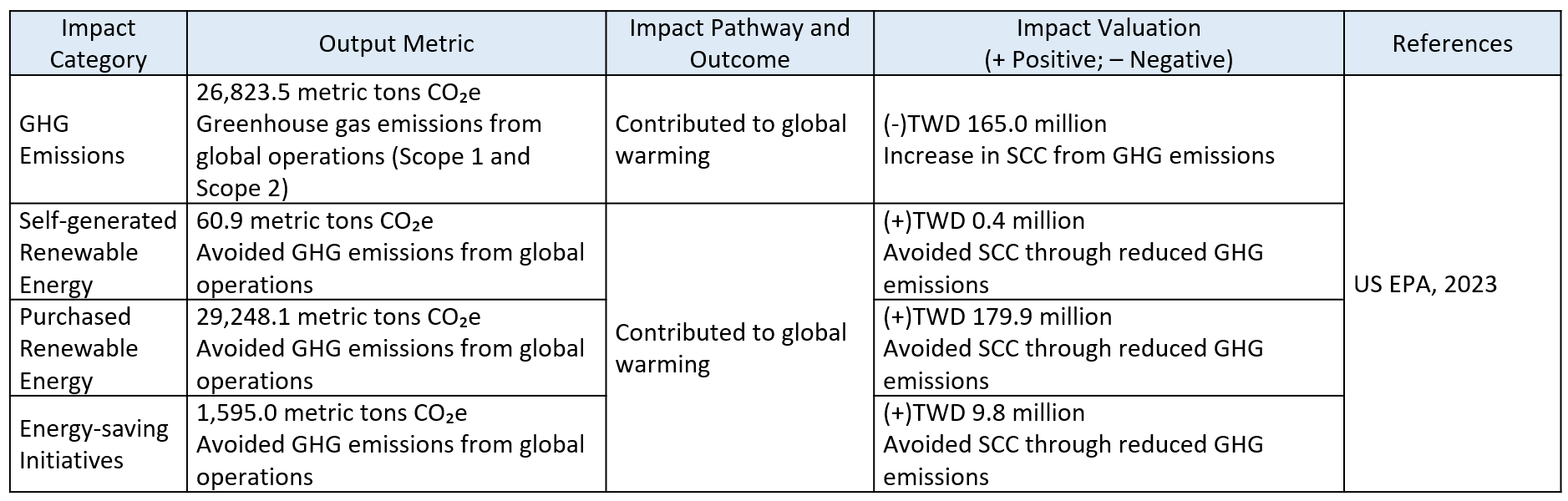
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are an inevitable part of corporate operations. These gases absorb and trap heat in the Earth’s surface and troposphere, leading to the greenhouse effect and intensifying global warming.
For Energy and Greenhouse Gas Management, greenhouse gas emissions from company operations create negative externalities that are materially relevant to the environment, as they directly contribute to global warming and impose long-term environmental costs measured through the Social Cost of Carbon (SCC). At the same time, E Ink’s actions to generate renewable energy for internal use, purchase renewable energy, and implement energy conservation initiatives produce positive external impacts. These measures reduce reliance on fossil fuels, avoid greenhouse gas emissions, and conserve natural resources, thereby mitigating climate change and supporting the global transition toward sustainable energy systems. Collectively, these outcomes demonstrate the material relevance of both emission-related risks and mitigation actions to external stakeholders and highlight the dual importance of managing impacts while creating environmental benefits.
From an Environmental Profit and Loss (EP&L) perspective, E Ink applies the Social Cost of Carbon (SCC) as the valuation coefficient per unit of GHG emissions. This approach estimates the long-term damages that climate change inflicts on global physical and economic systems, as well as the efforts required for energy transition to limit temperature rise. E Ink recognizes its responsibility in climate action and has committed to achieving 100% renewable energy use by 2030 (RE100) and net-zero GHG emissions by 2040, ensuring that business growth and environmental protection advance hand in hand.
To achieve these goals, the Company has progressively implemented management systems such as GHG Inventory (ISO 14064-1), Energy Management System (ISO 50001), Environmental Management System (ISO 14001), and Zero Waste to Landfill Verification (UL 2799). Meanwhile, E Ink continues to promote energy-saving and carbon-reduction initiatives and increase the proportion of renewable energy used, thereby steadily reducing GHG emissions and moving toward its long-term sustainability vision.